2024 EU AI Development Policy Research: The EU provides resources to support the development of AI startups through an innovation sandbox under the regulatory policy of the AI Act
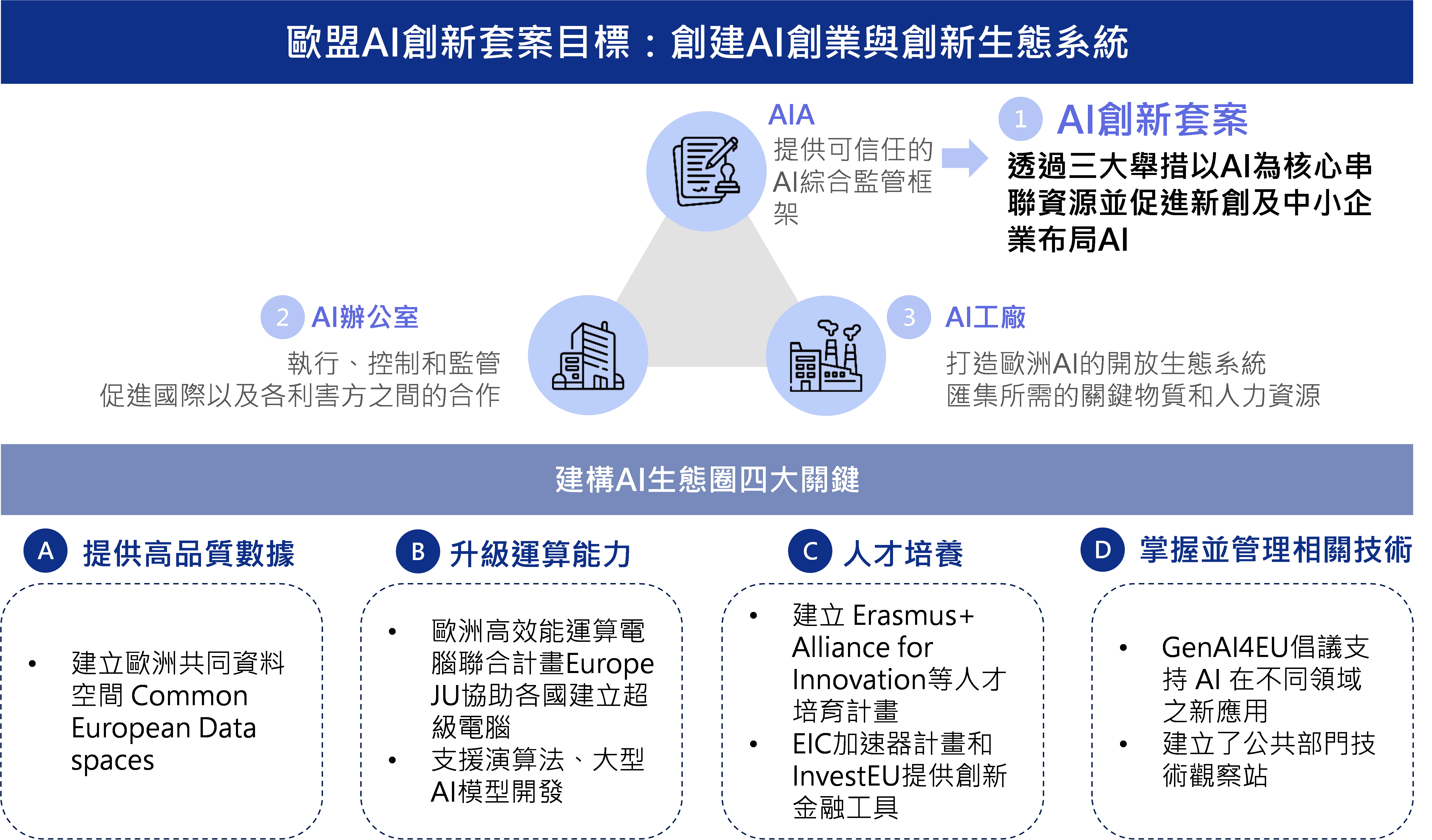
Figure Summary of the EU's "AI Innovation Package"
The EU's earliest AI industry promotion policy can be traced back to 2018, when the EU launched the "European Strategy for AI" and proposed the "Coordinated Plan on AI," "General Data Protection Regulation" (GDPR), "AI White Paper," and "European Data Strategy" to implement the strategy. This established the EU's overall AI development strategic framework. In this background, due to the influence of the two major AI powers, the United States and China, at the time, and the fact that the EU hopes to catch up quickly, despite its own AI industry just starting out, the EU proposed the "AI Act" (AIA) in April 2021. The EU hoped to strengthen the implementation of the EU strategy at the legal level, in order to achieve the goal of leading global AI governance. The EU introduced new laws and regulations or updated existing ones on this basis in 2022-2023, such as the "AI Liability Directive (AILD)," "Product Liability Directive (PLD)," and "AI Innovation Package," in hopes of supporting industrial development through industry promotion policies that take into account both supervision and the spirit of innovation before the AIA takes effect.
In addition to regulatory policies, the "AI Innovation Package" launched on January 24, 2023 is the EU’s approach to developing the AI industry. The package is in response to the initiative proposed by the President of the European Commission in the State of the Union Address on September 13, 2023.
In terms of computing power, European supercomputers are provided to innovative European AI startups to train their trustworthy AI models. Immediately afterwards, the European Union launched the Large AI Grand Challenge on November 16, 2023, and revised rules of the European High-Performance Computing Joint Undertaking (EuroHPC JU) to provide AI start-ups with financial support and the opportunity to use the computing power of supercomputers, encouraging European startups with experience in large-scale AI models to participate. These startups will be able to use EuroHPC supercomputers to develop large-scale AI models and eventually release open source model results for non-commercial use as a first step to implement the new initiative. In addition, it will also assist in upgrading supercomputers, allowing EuroHPC to establish supercomputers hosted in various countries in the EU and connect them to form an efficient supercomputer network, such as Spain's MareNostrum 5 and Luxembourg's MeluXina, which have been used for scientific research in the past, but were not optimized for work related to generative AI models. In addition, the upgrade will face GPU procurement issues, and the EU will strengthen procurement and obtain GPU chips in compliance with the Chips Act.
In terms of data, the policy document "Facilitating the development and innovation of trustworthy AI startups in the EU" was proposed, which will provide high-quality data accumulated in the Common European Data Spaces Project in the past, including health, media, transportation, agriculture, construction, environment, manufacturing, and R&D. The data can be combined individually or across fields through business-to-business (B2B) and business-to-government (B2G), in order to drive innovation and achieve the goal of eliminating data localization restrictions across the EU. Next, the European Commission will also establish data protection mechanisms for shared data, clarify responsibilities for incorrect data, data loss and revision standards, and assist in resolving disputes.
Therefore, in summary, the EU adopts a two-pronged approach when it comes to the development of the AI industry. On the one hand, it improves the supervision of AI systems from a legal perspective, including AIA for prevention beforehand, and AILD and PLD for remedy afterwards, so that victims can seek compensation with a clear legal basis. On the other hand, it actively promotes innovation and supports AI startups that have potential and the overall industry by providing computing resources and high-quality data.