【2021 Application Example】 AI Analysis Cloud Service Platform for Remote Sensing Big Data Enables the Smooth Application of Satellite Remote Sensing Images
Although satellite remote sensing images can make all surface objects visible, it still requires a lot of time and manpower to be truly applied to the industry. In order to effectively solve the problems that customers face in digesting huge amounts of image data and eliminate technical obstacles for cross-domain users to process satellite remote sensing images, ThinkTron has developed an "AI Analysis Cloud Service Platform for Remote Sensing Big Data" as a new beginning for cross-domain AI applications for spatial information.
In recent years, in response to the impact of industrial globalization, Taiwan's agriculture has continued to transition towards technology-based and higher quality, improving the yield and quality of crops by solving problems, such as microclimate impacts and pest and disease control. The demand of agriculture on images has expanded endlessly to accurately grasp the growing environment of crops. In the early years when UAVs (unmanned aerial vehicles) were not yet popular, manual field surveys were the most basic but most labor-intensive work. With the emergence of UAV drones, aerial photography operations might not be difficult, but the range that can be photographed is limited. Furthermore, surveying expertise is required to accurately capture spatial information. At this time, the use of satellite remote sensing data may break away from the past imagination of using image data.
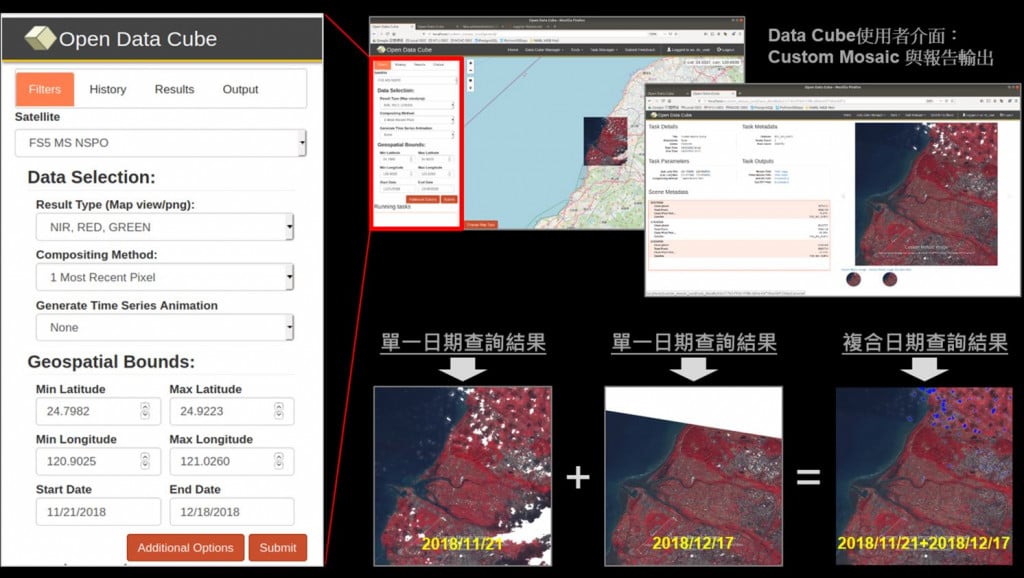
▲ Taiwan Space Agency (TASA) ODC data warehouse services
In the past ten years, with the breakthrough of modern satellite remote sensing application technology, Digital Earth has become a new trend in global data collection. Countries have developed data cube image storage technology, and the development of smart agriculture has become one of the largest image users. Determining planting distribution is the first step in understanding crop yields. Free satellite remote sensing images, powerful data warehousing support, and the team's robust image recognition technology are important supports for accelerating agricultural transformation.
Using satellite remote sensing image data can accelerate the development of smart agriculture.
However, in the past, it was difficult to extract large-area crop distribution through satellite remote sensing images, not to mention the cost. If you wanted to use free information, you had to visit all websites of international space agencies, look through the wide variety of satellite specifications, and carefully evaluate the sensor specifications, image resolution, and revisit cycle. After finding suitable images, you had to look at them one by one to filter the ones you need. Next is downloading dozens of images that are often several hundreds of Megabytes (MB) each, which might exceed the capacity of your computer.
Also, after overcoming image access and preparing data, you must then start to confirm the downloaded image products and which bands you want, because the image you see is not just an image file (.jpg or .png), but rather complex multi-spectral information, attribute fields and coordinate information. It takes a lot of effort just to confirm the correct information. Facing GIS software packages with complex functions is the start of another trouble. The complex image pre-processing process and the inflexible machine learning package greatly reduce the efficiency of analyzing data. After finally getting the results of crop identification, you might find that the best time for using map information may have already passed. The above-mentioned complex and time-consuming satellite image processing problems are precisely the pain points of the market. ThinkTron expanded from traditional machine learning to modern deep learning applications, and developed an "AI Analysis Cloud Service Platform for Remote Sensing Big Data" under the GeoAI framework, breaking through the constraints of details in the spatial information for customers.
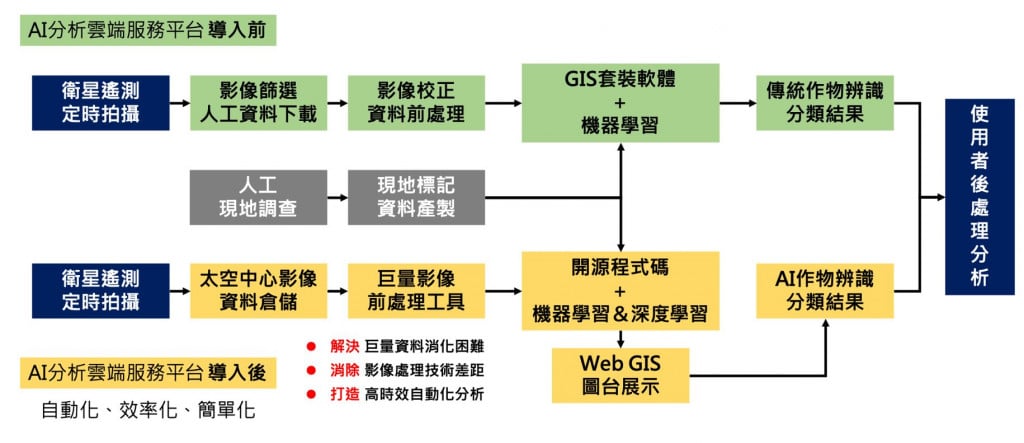
▲Differences between the process before and after introducing the AI analysis cloud service platform
ThinkTron said that Taiwan's ODC (Open Data Cube) system has been completed and began providing services after years of efforts from the Taiwan Space Agency (TASA), formally becoming aligned with international trends. The powerful warehousing technology allows users to easily capture and use image data of a specific time and spatial range according to their needs. The warehouse stores multiple satellite image resources from international space agencies, including the ESA's Sentinel-1 (one image every 6 days), Sentinel-2 (one image every 6 days), USGS's Landsat-7 (one image every 16 days), Landsat-8 (one image every 16 days), and the domestic Formosat-2 (one image every day) and Formosat-5 (one image every 2 days).
ThinkTron develops satellite image recognition tools based on Python
Breaking free from the limitations of GIS (Geographic Information System) software packages, ThinkTron integrated GDAL (Geospatial Data Abstraction Library) based on Python, and considered computing efficiency and parallel processing when developing all tools required for satellite image processing and image recognition modeling, including coordinate system and data format conversion, grid and vector data interaction, and data intra-difference and normalization. All of the tools are designed with AI applications in mind, and some commonly used tools are packaged into an open source package under the name TronGisPy to benefit the technical community. ThinkTron utilized the team's understanding of satellite remote sensing images and the collected tagged data (crop distribution maps) to preset the image recognition modeling process, the required training data specifications, and dataset definitions. This is imported into the machine learning (LightGBM) or deep learning (CNN) framework that was completed in advance, and the entire training process to be performed in the Web GIS interface, providing users with partial flexibility to freely filter images, confirm spatial and temporal ranges, select models, and adjust hyperparameters. In addition to the operation of training models, it also provides historical models to output identification results, and finally displays the identification results of crop distribution on the Web GIS map.
In fact, agriculture is not the only industry that needs satellite remote sensing applications. AI applications of spatial information have also appeared in various fields as companies in different industries aim to enhance their global competitiveness. For example, surveying and mapping companies that have a large amount of map data can use the AI analysis cloud service platform to store map data while also accelerating the efficiency of digital mapping. Under the severe global climate change and the risk of strong earthquakes, there is a wide variety industrial insurance, agricultural insurance, financial insurance, or disaster insurance are all inseparable from spatial information. The use of remote sensing image recognition to understand insurance targets has long been an international trend.
▲ AI Analysis Cloud Service Architecture for Remote Sensing Big Data